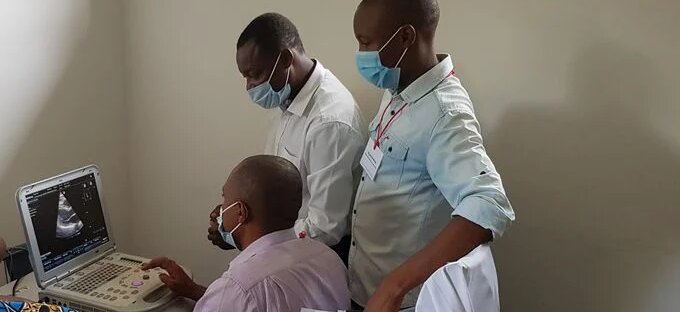
Swiss TPH "Tuberculosis (TB) remains one of the world’s biggest infectious disease killers. It is a complicated disease to diagnose and treat, even more so when it affects organs outside of the lung. A clinical trial in Tanzania tested a diagnostic algorithm including point-of-care ultrasound to increase the proportion of correctly managed patients. While the proportion of correctly managed patients could not be increased, the study indicates that this diagnostic algorithm could be a feasible approach to increase confirmation of TB. This is the first clinical randomized controlled trial successfully conducted at the St. Francis Referral Hospital in Ifakara, highlighting the excellent clinical research knowhow and collaboration between the Ifakara Health Institute, Swiss TPH, and other partners. The results were published in the peer-reviewed journal Clinical Infectious Diseases."